Waves are the way in which energy is transferred. Of the many different types of waves, some can be divided into either transverse or longitudinal waves. Definitions: For Longitudinal waves, the displacement of the medium is parallel to the direction of propagation of the wave (direction of the wave's travel) For Transverse waves, the.. Characteristics of longitudinal and transverse waves. Google Classroom. Below is an image of a transverse wave through a medium where the dashed line is the medium's equilibrium position. What does the arrow represent? Use a coordinate system where upward is the positive direction for medium displacement.

Difference between Longitudinal Waves and Transverse Waves Types of Waves Physics Terms

Difference between Transverse Waves and Longitudinal Waves Wave Motion 2 YouTube

PPT University Physics Waves and Electricity PowerPoint Presentation ID327483
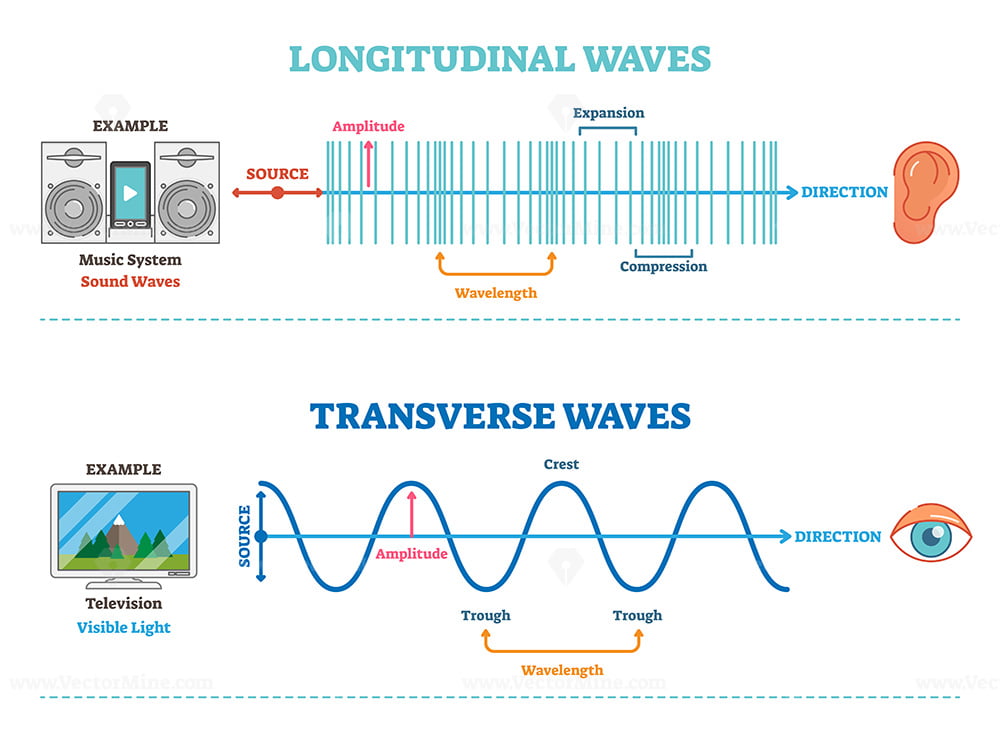
Types of longitudinal, transverse and surface waves examples outline diagram VectorMine

How are Longitudinal Waves Related to Transverse Waves? YouTube

mr i explains The Difference between Transverse and Longitudinal Waves YouTube
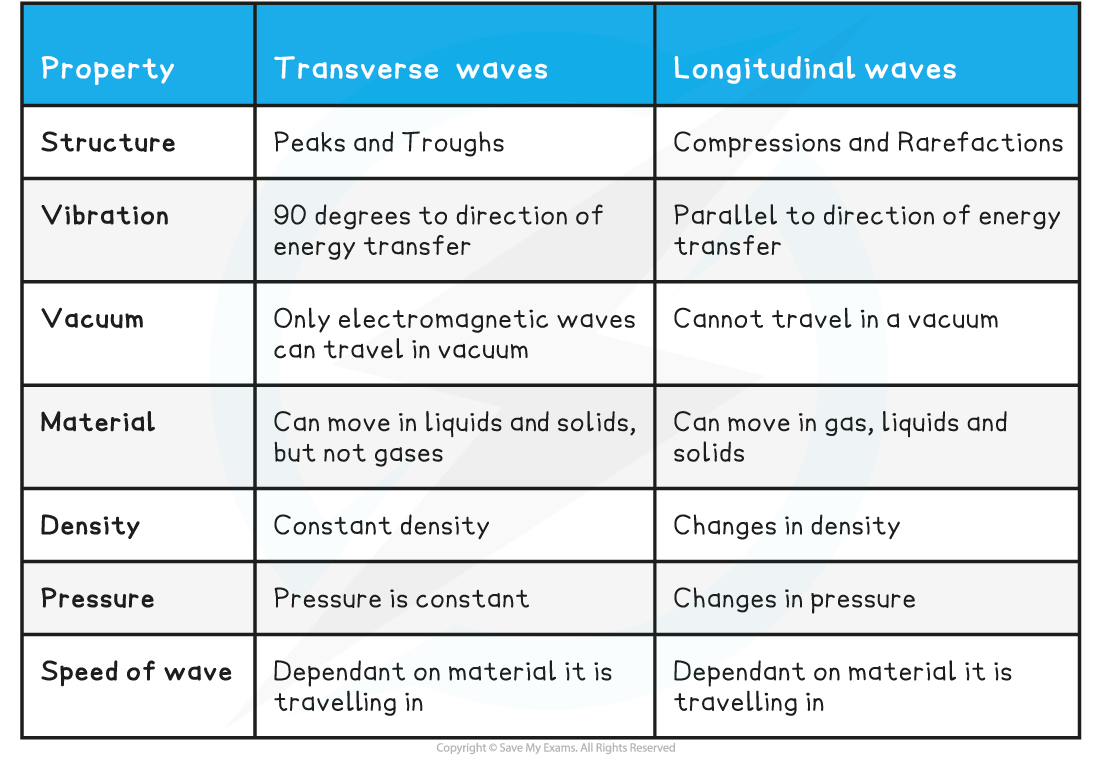
Edexcel IGCSE Physics 复习笔记 3.1.1 Transverse & Longitudinal Waves翰林国际教育

Transverse Waves vs Longitudinal WavesDifference between transverse and longitudinal waves

PPT Properties of Waves (Part 2) PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2481020

GCSE Physics Longitudinal and Transverse Waves YouTube
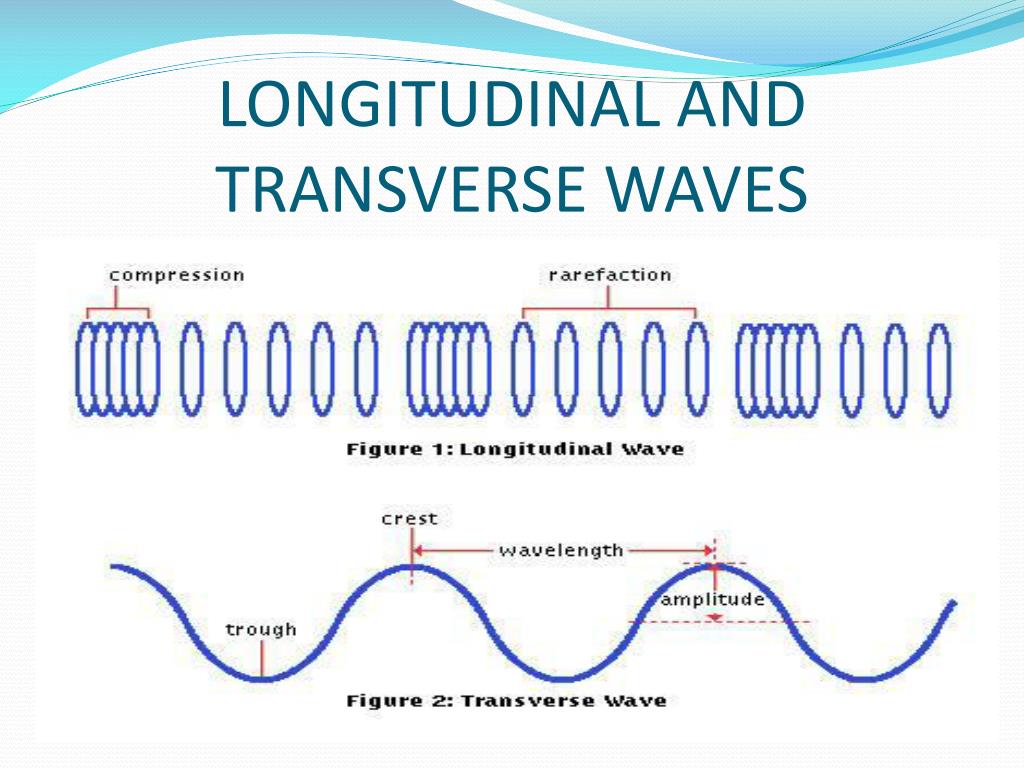
PPT Waves and Tides PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5422522

Waves Basic Definition, Transverse vs. Longitudinal, Mechanical vs. IB
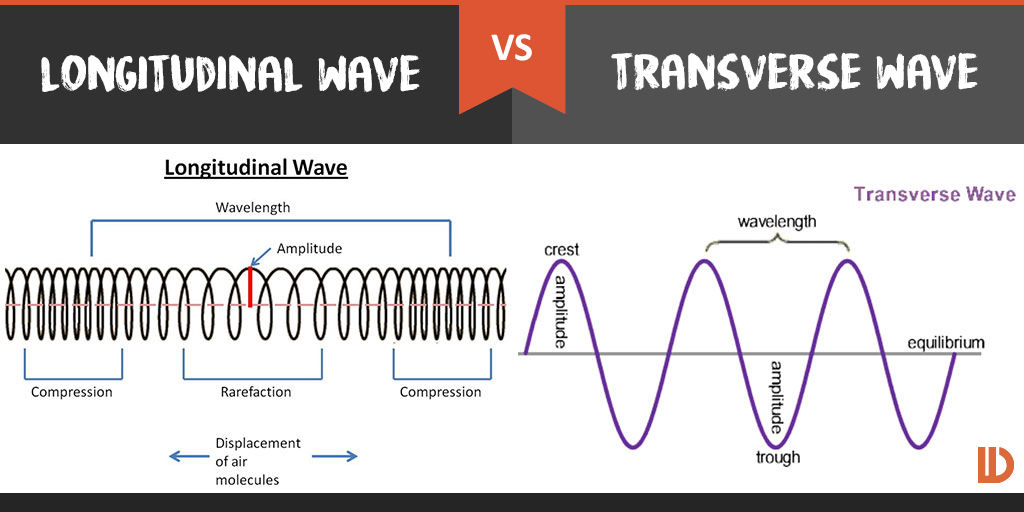
What is the difference between a longitudinal wave and a transverse wave? Socratic

How Are Transverse and Longitudinal Waves Alike and Different BricegroBuck
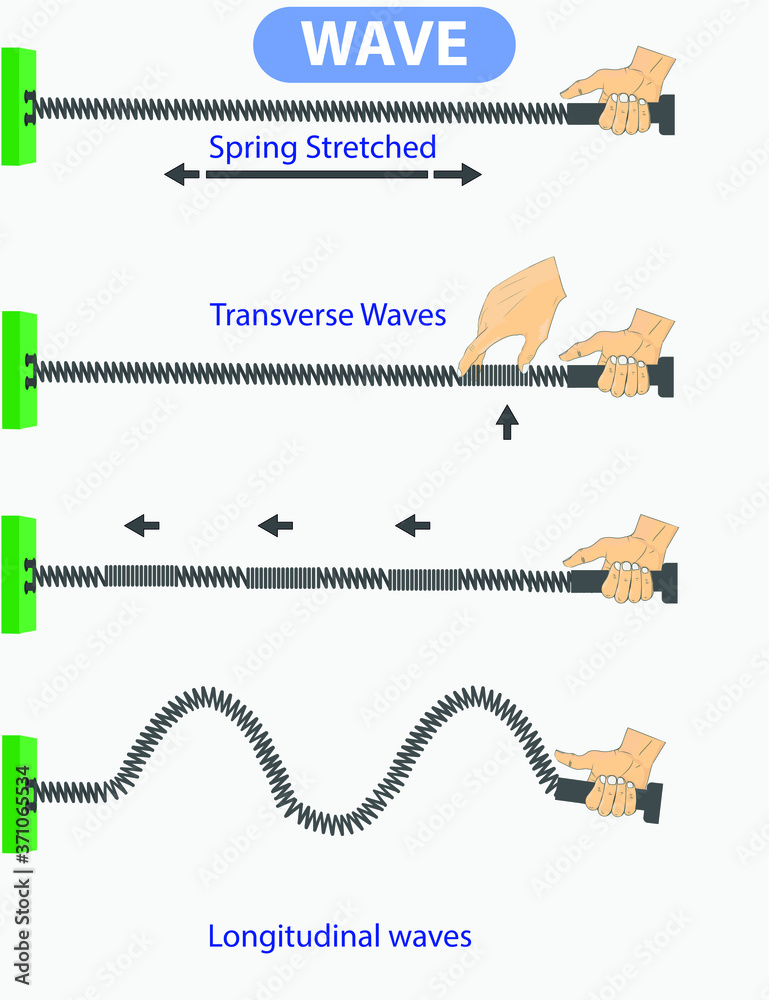
physics. spring stretched. transverse waves. longitudinal. The difference between throwing and
Transverse and Longitudinal Waves

Longitudinal and Transverse Labster
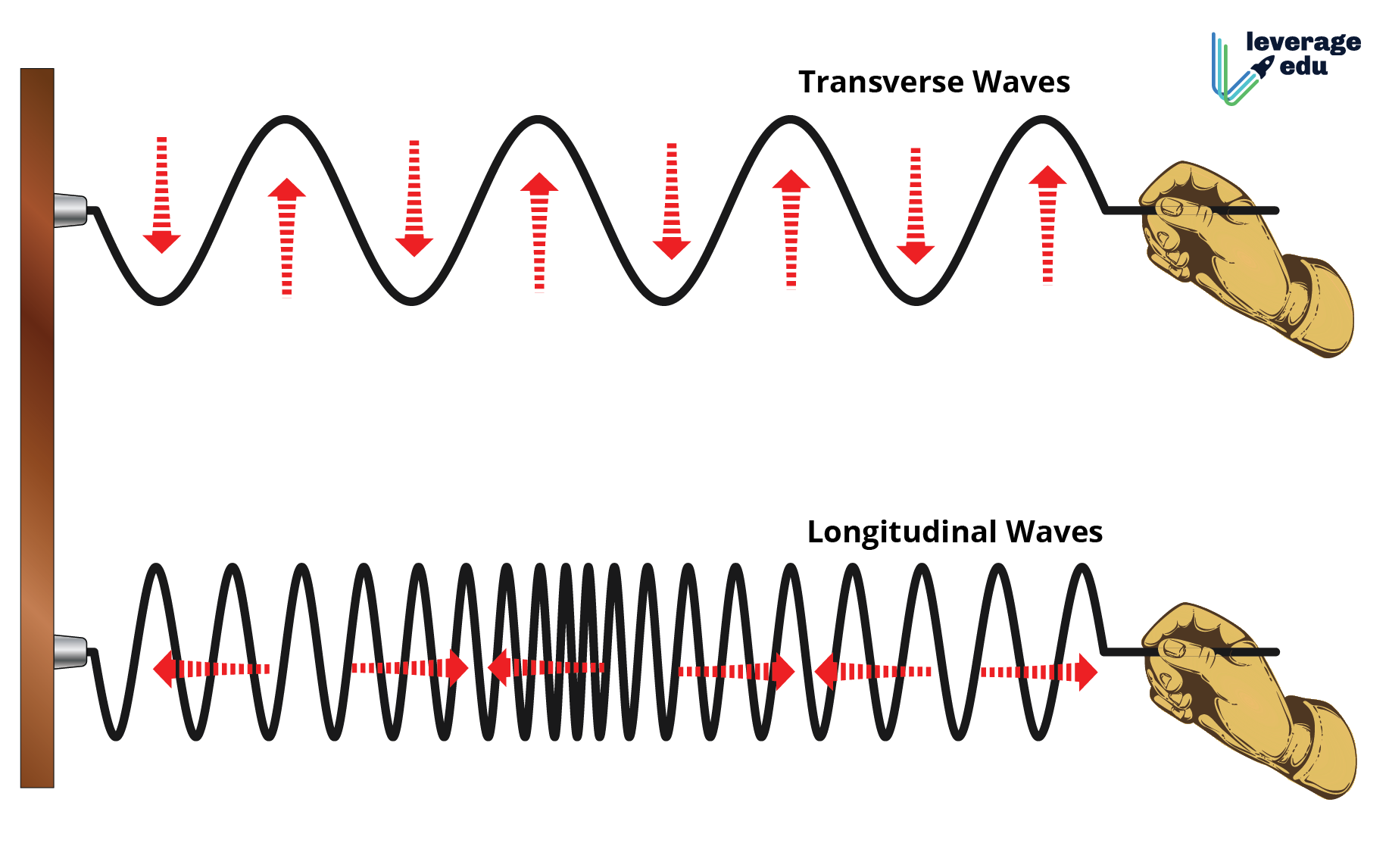
Transverse vs Longitudinal Wave Leverage Edu

Longitudinal and Transverse wave type, vector illustration scientific diagram Waves, Science
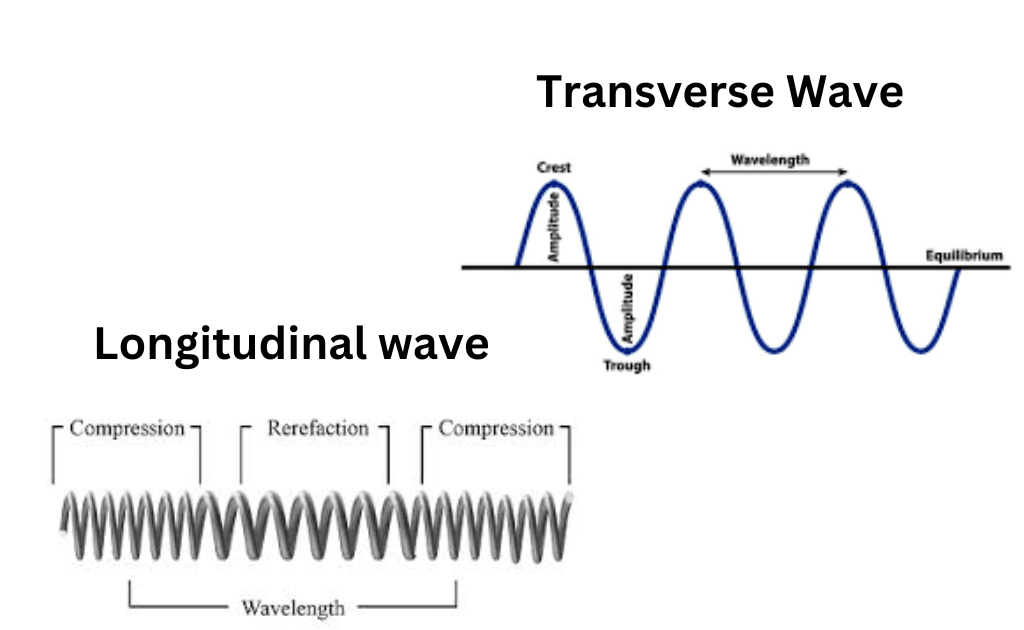
Difference between Longitudinal and Transverse Wave
Transverse waves are defined as: Waves where the points along its length vibrate at 90 degrees to the direction of energy transfer. For a transverse wave: The energy transfer is perpendicular to wave motion. They transfer energy, but not the particles of the medium. They can move in solids and on the surfaces of liquids but not inside liquids.. Examples include gamma rays, X-rays, ultraviolet waves, visible light, infrared waves, microwaves, and radio waves. Electromagnetic waves can travel through a vacuum at the speed of light, v= c =2.99792458 × 108m/s. v = c = 2.99792458 × 10 8 m/s. For example, light from distant stars travels through the vacuum of space and reaches Earth.